PnP grids - Grid-forming control for distributed power converters
The Committee on Education, Research and Technology Assessment of the German Bundestag dealt with the threat to modern societies posed by large-scale and long-lasting power outages. It was emphasized that regional island grids with decentralized energy suppliers are of great importance for disaster management, especially for the supply of central infrastructure elements such as authorities and hospitals.
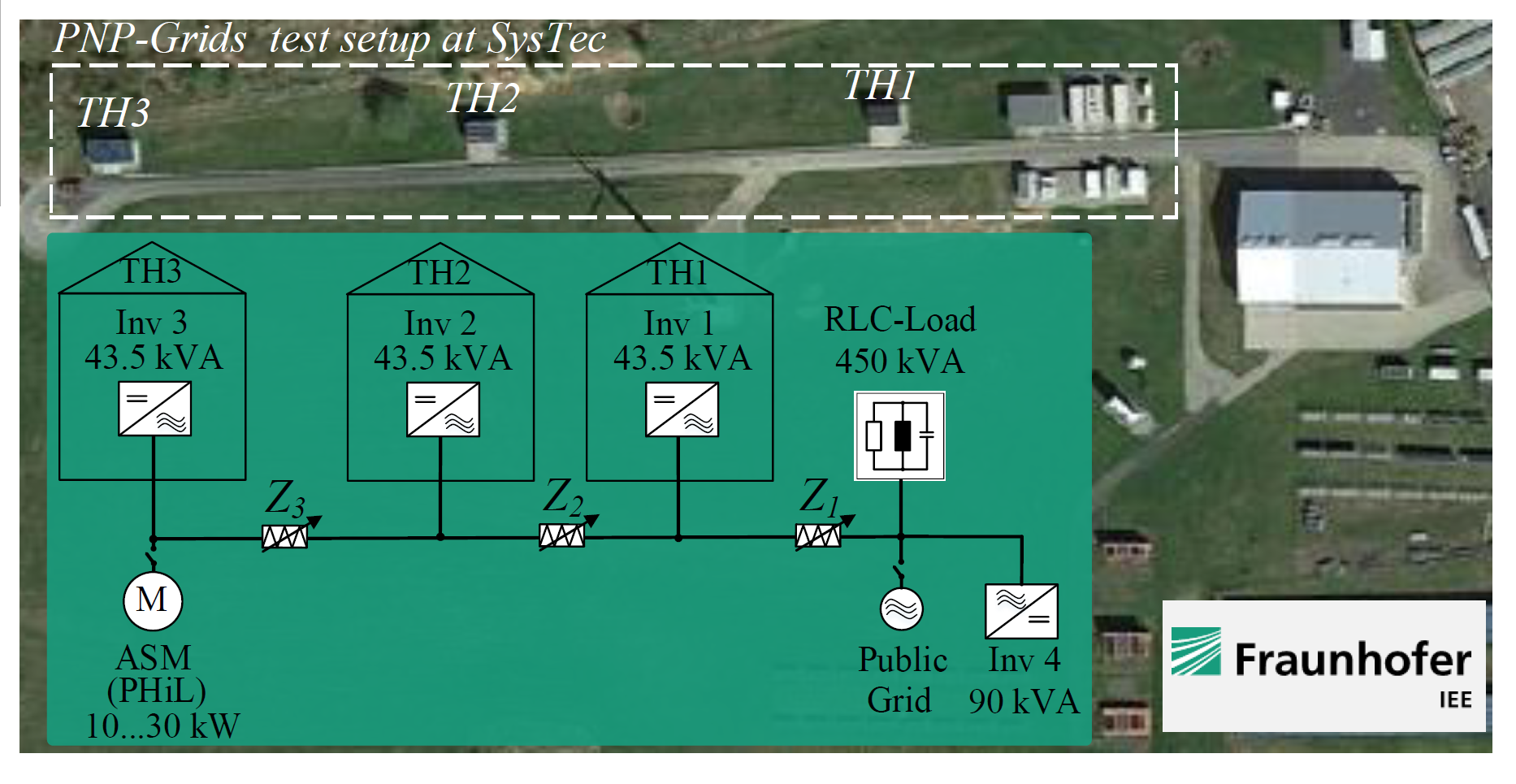
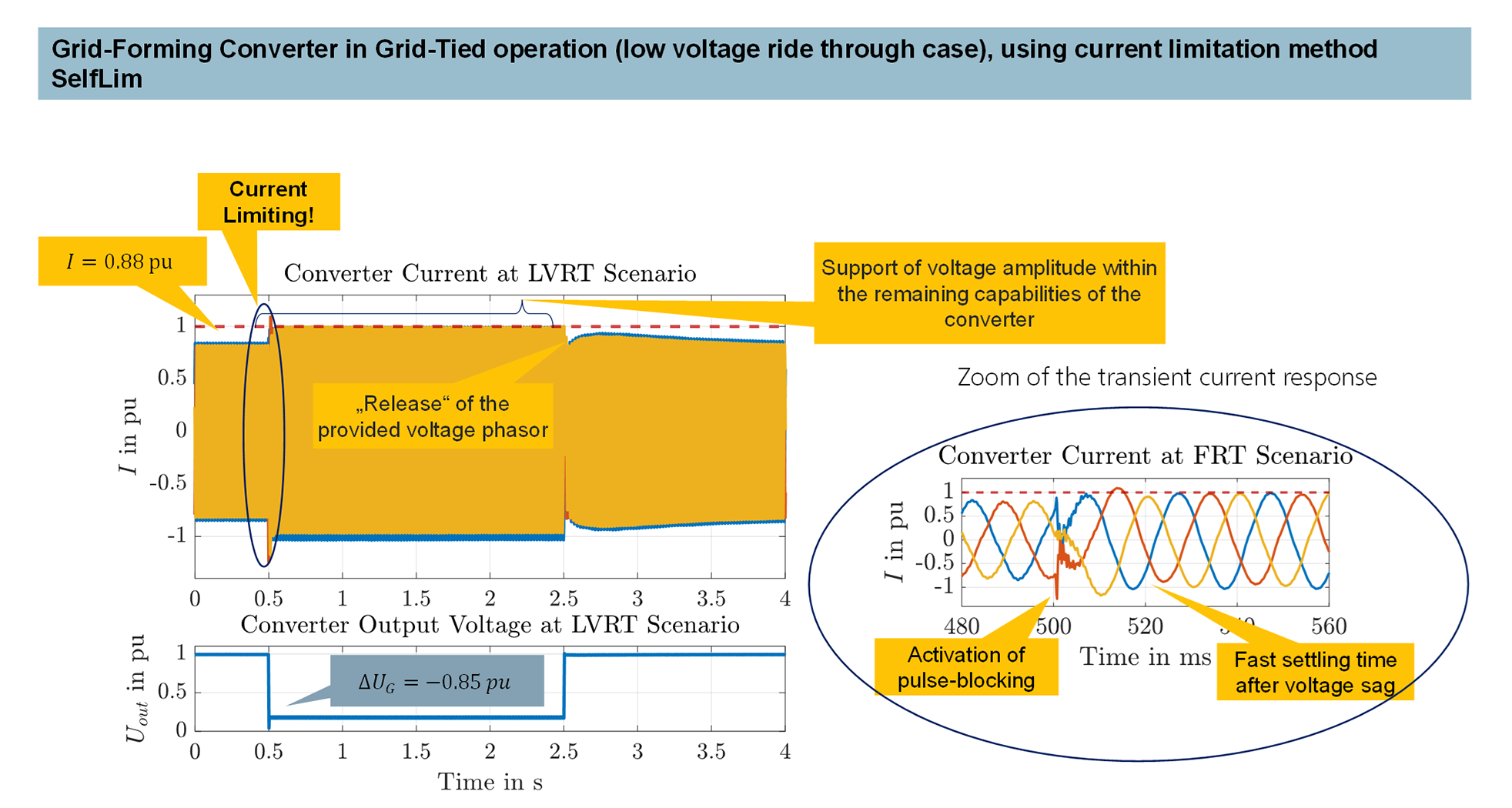
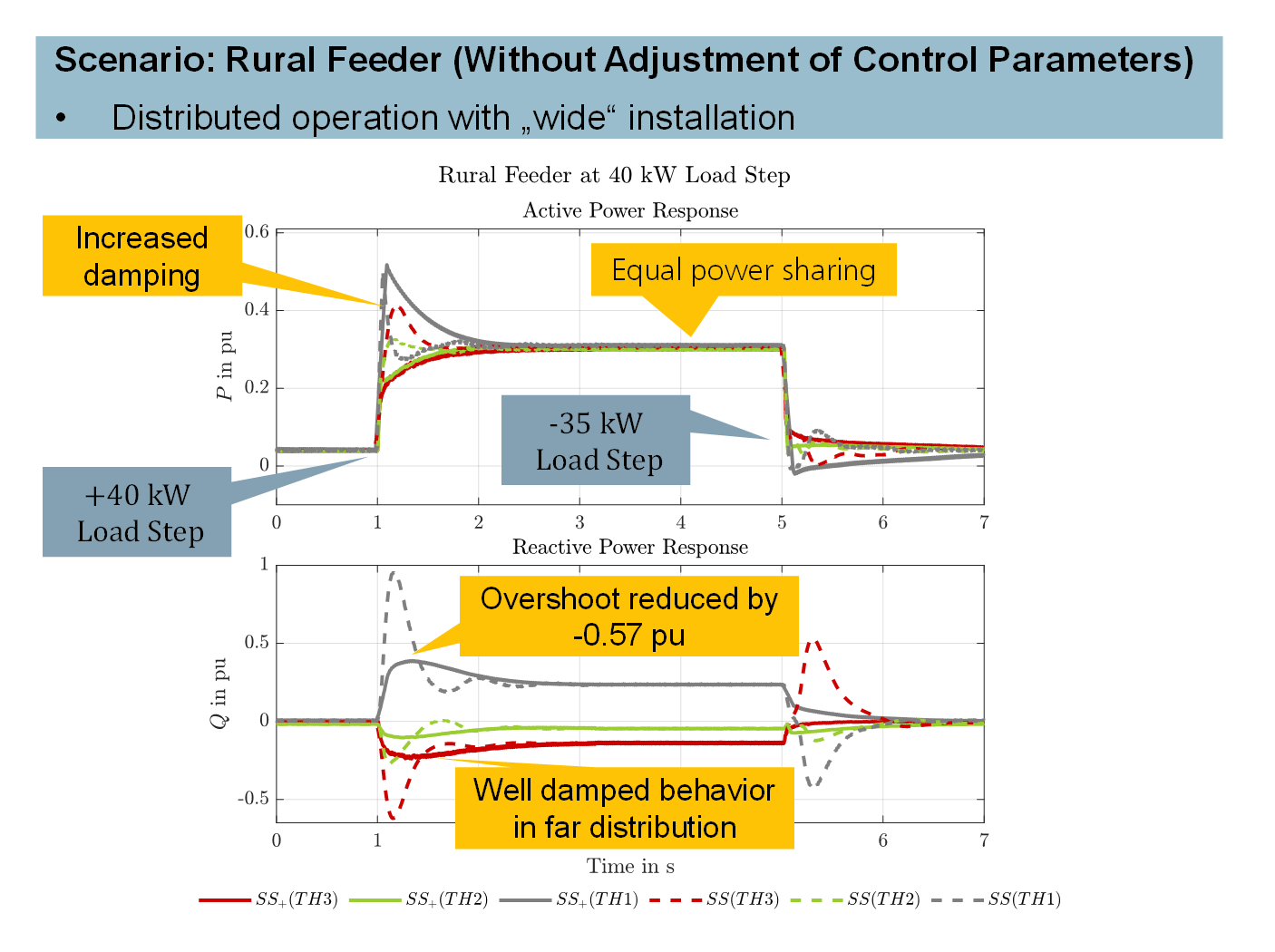
Fraunhofer IEE presented an innovative solution for the construction of stand-alone grids, which used grid-forming power converters that could operate locally autonomously, modular and without higher-level communication. These power converters were also intended to improve power quality and were used in industrial plants, emergency power supplies for public facilities and hospitals. In order to increase redundancy and modularity in island grids and interconnected grids, it was crucial that the grid-forming power converters could be distributed flexibly in the grid. The social benefit of this control method was considered to be high, as it offered solutions to the challenges of island and future supply grids.